-
2Se mentre passeggiamo in un parco, proviamo a cimentarci con qualche attrezzo ginnico, potrebbe capitare che uno di questi sia…Spunti potenzialmente utili senza AI (AI free)29 Settembre 2024
-
2The race of research to obtain new therapeutic paths in Medicine, especially for tumor diseases, sometimes takes on a spasmodic…English Version25 Agosto 2024
-
2La corsa della ricerca per ottenere nuovi percorsi terapeutici in Medicina, soprattutto per le malattie tumorali, talora assume un ritmo…Prospettive future14 Agosto 2024
-
3Gli Ultrasuoni (US) sono onde pressorie acustiche che non sono percepite dall’orecchio umano e si diffondono nei tessuti che compongono…Prospettive future8 Agosto 2024
-
4Le terapie antitumorali a volte producono effetti avversi significativi sugli occhi [1,2], che possono danneggiare la vista del paziente a…Terapie e metodiche di cura4 Luglio 2024
English Version
Osteosarcomas: the future perspective of therapy with Nanoparticles combined with the sonodynamic action of Ultrasound.
The race of research to obtain new therapeutic paths in Medicine, especially for tumor diseases, sometimes takes on a spasmodic pace, especially when it enters completely innovative scientific sectors, produced only in recent decades. As already illustrated in some of the articles previously published on this site, Nanotechnologies represent a new world, full of promising […]
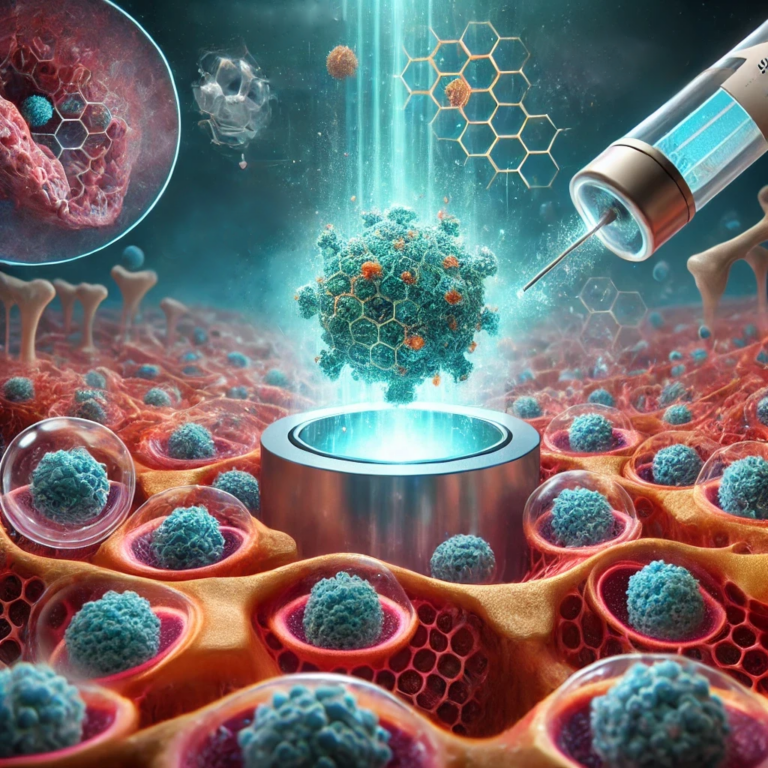
The race of research to obtain new therapeutic paths in Medicine, especially for tumor diseases, sometimes takes on a spasmodic pace, especially when it enters completely innovative scientific sectors, produced only in recent decades.
As already illustrated in some of the articles previously published on this site, Nanotechnologies represent a new world, full of promising solutions for numerous diseases.
Research today cannot be limited to watertight compartments, it requires continuous osmosis, a close exchange of notions and collaborations between the various researchers, composing groups that aim at ambitious and innovative goals:
this is why doctors, biologists, chemists, physicists and therefore bioengineers and others enter the field.
Our heartfelt thanks and our fervent encouragement should go to all those who in silence, under the lights and artificial environments of the laboratories, carry out their projects with hard effort and tenacity, for the advancement of health and treatments.
We then come to deal with a therapeutic possibility envisaged using Nanotechnologies for a dramatic tumor disease, Osteosarcoma: both for the therapeutic side and for the consequences that can afflict the individual, even after recovery.
Osteosarcomas: a possible role of nanoparticles therapy combined with the sonodynamic action of Ultrasound.
Marco Carofiglio, Marzia Conte, Prof.ssa Valentina Cauda – TNH lab Politecnico di Torino
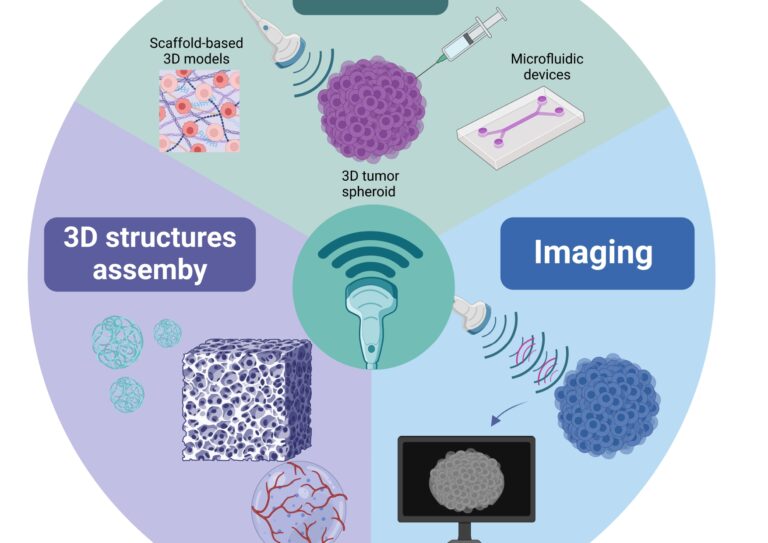
Bone cancer is a rare and difficult-to-treat disease, especially concerning since 3-5% of cases occur in adolescents and children. Treating bone osteosarcoma without invasive techniques and avoiding limb amputation is an extremely difficult challenge. The deep location of the tumor within the bones often makes it difficult for external treatments to reach the affected area. However, ultrasound therapies have shown promise in overcoming these barriers.
This study highlights the potential of iron-doped ZnO (FZ) nanoparticles as potent sonosensitizing agents for the treatment of bone osteosarcoma using 3D models of osteosarcoma in spheroid form.
These FZ nanoparticles have been engineered to be biocompatible through an innovative phospholipid formulation, enabling bioconjugation of virtually any targeting entity. To increase specificity towards osteosarcoma cells, we incorporated a targeting peptide that recognizes hepatocellulin receptor-2 (EphA2), a protein that is highly overexpressed in these tumors.
Our study introduces a pioneering sonodynamic therapy for bone osteosarcoma, using biocompatible FZ nanoparticles that can be remotely activated by safe levels of ultrasound.
The uniqueness of our research lies in the use of these biomimetic and targeted nanoparticles, which demonstrate exceptional efficacy as stimulus-sensitive nanomedicines under acoustic pressure. In addition, our work highlights the increased safety provided by the innovative lipid coating of our metal oxide nanocrystals. This coating optimizes the interactions of these hybrid nanoparticles with recipient cells, even in complex 3D models, ensuring rapid and efficient internalization and intracellular distribution.
In essence, not only does it present a new therapeutic avenue for bone osteosarcoma, but it also lays the foundations for future advances in targeted nanomedicine.
Link : https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2024.109826